Yijun Qi’s group reports a role for MINIYO (IYO) and QUATRE-QUART 2 (QQT2) in the assembly of RNA Polymerases II, IV and V in Arabidopsis
On January 21, 2018, Prof. Yijun Qi’s group from School of Life Sciences at Tsinghua University published a research article in The Plant Cell, reporting a role for IYO and QQT2 in the assembly of RNA Polymerases II, IV and V in Arabidopsis.
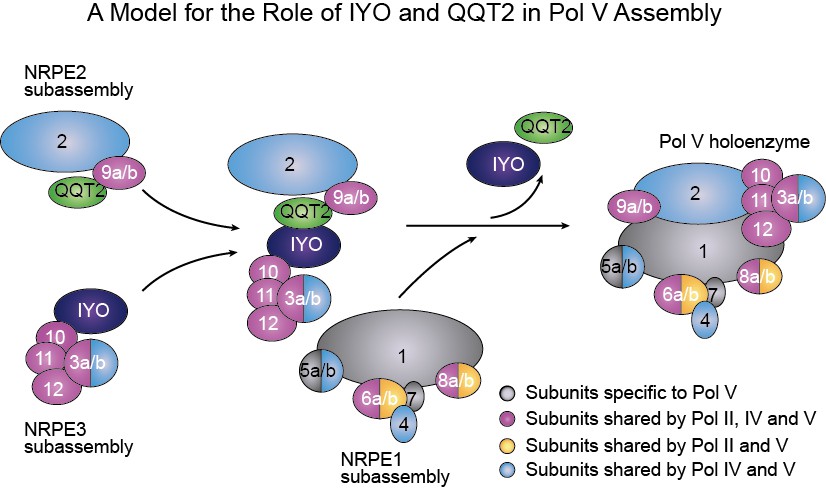
DNA methylation, an important epigenetic modification, is established through an RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) pathway. RNA POLYMERASE IV (Pol IV) and Pol V generate 24-nucleotide (nt) siRNAs and long intergenic noncoding (IGN) RNAs, respectively, in RdDM. Pol IV-dependent siRNAs are primarily incorporated into ARGONAUTE (AGO4). AGO4/siRNA complexes and IGN RNAs direct the recruitment of DOMAIN REARRANGED METHYLTRANSFERASE 2 (DRM2) to target loci to establish DNA methylation. Pol IV and Pol V are evolved from Pol II and the subunit compositions of Pol IV and Pol V largely resemble that of Pol II. Pol IV, Pol V and Pol II each consist of 12 subunits, which are termed NUCLEAR RNA POLYMERASE D (NRPD), NRPE and NRPB (RPB in yeast and human cells) subunits, respectively. The assembly of Pol II in yeasts and humans involves the formation of RPB3, RPB2 and RPB1 subassemblies aided by assembly factors. However, little is known about how plant Pol II, Pol IV and Pol V subunits assemble.
In this study, Qi and colleagues identified mutant alleles of IYO, QQT2 and NUCLEAR RNA POLYMERASE B11/D11/E11 (NRPB/D/E11) in a forward genetic screening that aimed to identify mutants with compromised siRNA accumulation and GFP-AGO4 stability. They found that Pol IV-dependent small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and Pol V-dependent transcripts and genome-wide RdDM were greatly reduced in the mutants. Using label-free quantitative mass spectrometry and coimmunoprecipitation, they found that, NRPE1, the largest subunit of Pol V, failed to associate with other Pol V subunits in the iyo and qqt2 mutants, suggesting the involvement of IYO and QQT2 in Pol V assembly. Using yeast two hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation, they found that IYO and QQT2 directly interact. IYO and QQT2 were mutually dependent for their association with the NRPE3 subassembly prior to the assembly of Pol V holoenzyme. Finally, they show that IYO and QQT2 are similarly required for the assembly of Pol II and Pol IV. Their findings reveal IYO and QQT2 as cofactors for the assembly of Pol II, Pol IV and Pol V and provide mechanistic insights into how RNA polymerases are assembled in plants.
Yaoxi Li, Yuxiang Yuan, Ph.D students, and Xiaofeng Fang, a postdoc, from School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, are first authors, and Dr. Yijun Qi is the corresponding author of this article. The study is funded by the National Science Foundation of China and Tsinghua University-Peking University Joint Center for Life Sciences.
Paper link:
http://www.plantcell.org/content/early/2018/01/18/tpc.17.00380